
A specific characteristic of the hair follicle is it reservoir function.
#Comsol 5.1 diffusion skin
Its importance was shown recently by a researcher as permeation is better in a skin area containing hair follicles and glands in comparison to an area without them. Since hair follicles and glands build only a small part of the human skin, their relevance for skin permeation was neglected for a long time. The appendageal route describes the penetration of a substance through skin appendages like hair follicles and glands. An important function of the tight junctions, which are formed during the differentiation of keratinocytes, is to protect the skin from water loss. They are located between the keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis. These are networks of strands which are formed by membrane proteins connecting cells. Another barrier in this intercellular space is the tight junctions. Because of the fatty acids, lipophilic substances can pass easier through the intercellular route in contrast to lipophobic substances.
#Comsol 5.1 diffusion free
The intermediate space consists of cholesterols, ceramides and free fatty acids. Īlternatively, there is a way through the intercellular spaces between the cells. Until now, it is not clear if hydrophilic substances choose this pathway. This is probably the most difficult way for substances, because they should have lipophilic and hydrophilic properties.

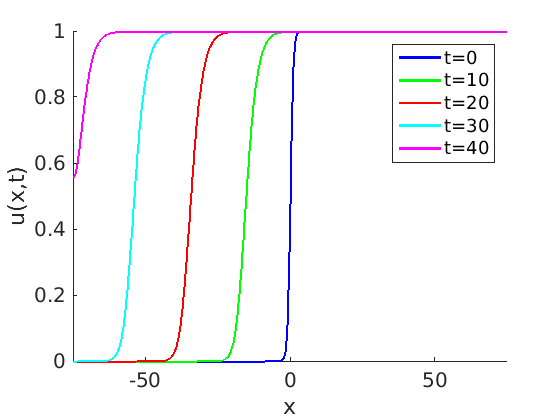
Here, the substances have to pass alternating lipophilic and hydrophilic layers. The transcellular route leads the permeating substances directly through the cells. Schematic illustration of the three possible pathways of a permeating substance through the stratum corneum. Substances such as drugs and chemicals penetrate through the skin barrier in three possible routes: the transcellular, the intercellular and the appendageal route (see Figure 1). The stratum corneum (horny layer) is the upper layer of the epidermis and forms the main barrier of the skin. The human skin consists of three layers, the epidermis, dermis and subcutis. If a concentration gradient exists, the particles move in the direction of lower concentration. Diffusion is the physical process of randomized particle movement. From a scientific point of view, it is the permeation of a substance through the skin layers. The permeation of the skin is the pathway of a substance from the surface to the blood vessel. The entering process and depth of substance penetration through the skin depends on the physical and chemical character of the substance and the skin. Penetration describes the entering of a substance into the skin. Penetration, diffusion and permeation through the skin
#Comsol 5.1 diffusion software
This software tool helps to describe the physical effects of the experimental set-ups more precisely and can further be used to reduce the required amount of experiments significantly.Ģ. The diffusion coefficient is estimated via parameter optimization performed in COMSOL Multiphysics. By this, the permeation coefficient of substances through a skin-tissue barrier can be determined. Then an alternative method based on skin tissue cultures in a membrane insert system is introduced. Therefore, this chapter will first give a brief overview of standard methods used to investigate permeation and diffusion on the skin. But this is indispensable, if multi-well test systems with several samples run in parallel or multi-organ-chips are applied. Most methods for determination of diffusion and permeability parameters have been developed for large biopsies and can hardly be applied for small-scale 3D skin tissue cultures. Especially the barrier function between artificial and human skin can differ, so permeation and diffusion investigation in this area is necessary. Artificial skin models based on human cells are intended to replace animal experiments. Furthermore, in 2013 the European Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 entered into force, which prohibits animal experiments for cosmetics products. The fact is that drug testing on human skin is more efficient in comparison to animal skin just like rat, mouse and guinea pig.
In this respect, human three-dimensional skin models have become an interesting tool.Īnimal experiments are still a common method of testing drugs and also for skin, which is ethically controversial, cost-intensive and time-consuming. Furthermore, permeability studies play an important role in toxicity tests applied in drug development as well as substance testing. This is evident for dermal drug delivery systems, where drugs can be applied in the form of creams or patches on the skin. Permeability studies are indispensable to characterize the transport of substances through the skin, either natural skin or cultivated 3D skin models.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
